null safety
런타임 시점에 null이 들어오게 되어 발생하는 에러를 방지하고자 함.
이전과 다르게 모든 자료형은 nullable(?)이 붙지 않는 이상 non-nullable로 취급됨.
dart의 타입 시스템이 바뀌었음
https://dart.dev/null-safety/understanding-null-safety
Understanding null safety
A deep dive into Dart language and library changes related to null safety.
dart.dev
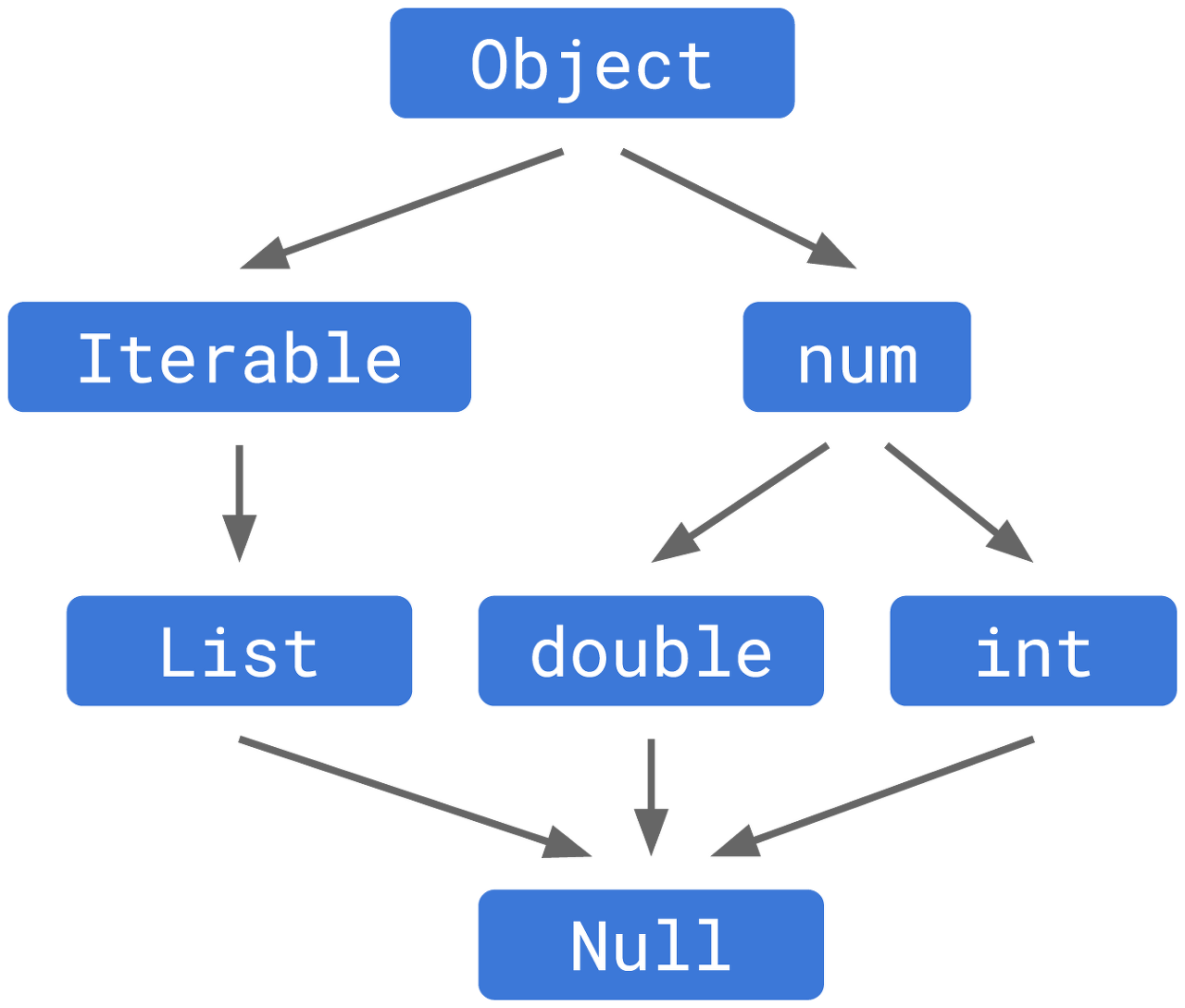
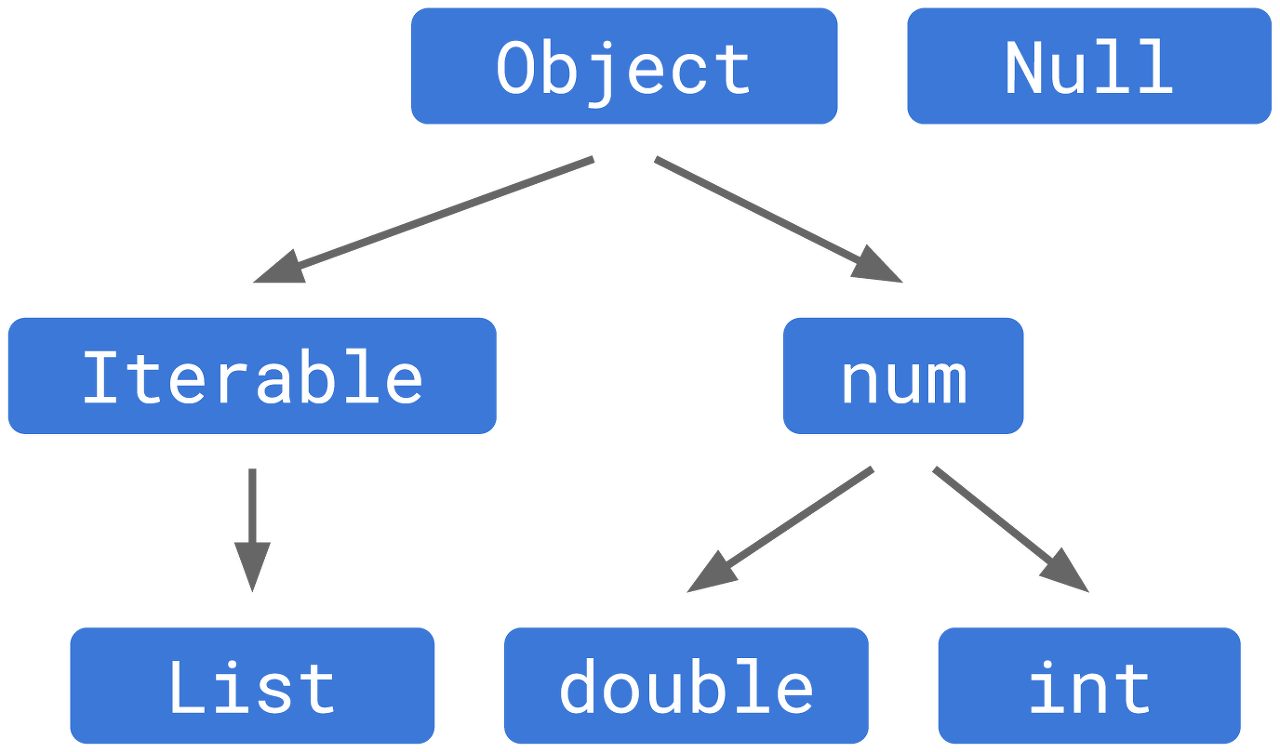
좌측이 null safety가 적용되기 전의 타입 시스템이라면 null safety가 적용되고난 후에는 우측처럼 되었다.
Null이 별도의 타입 처리된 것이다.
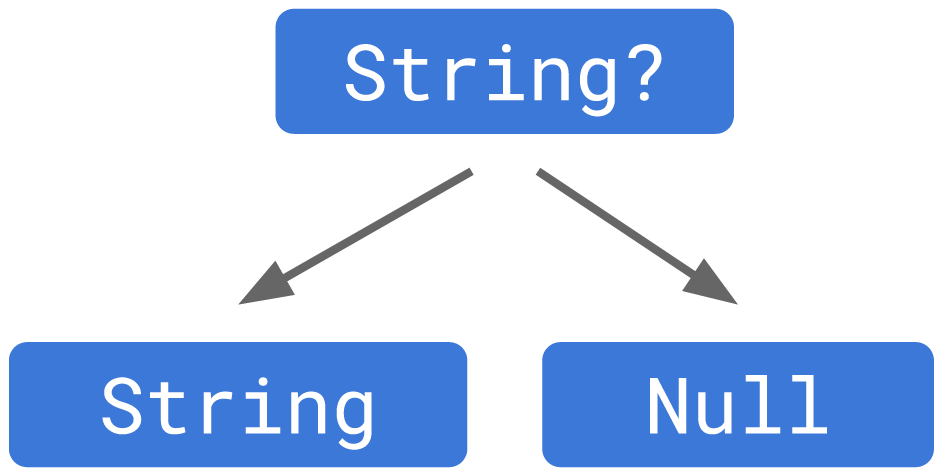
더 나아가 String? 꼴과 같이 nullable 타입을 지정하게 되었다.
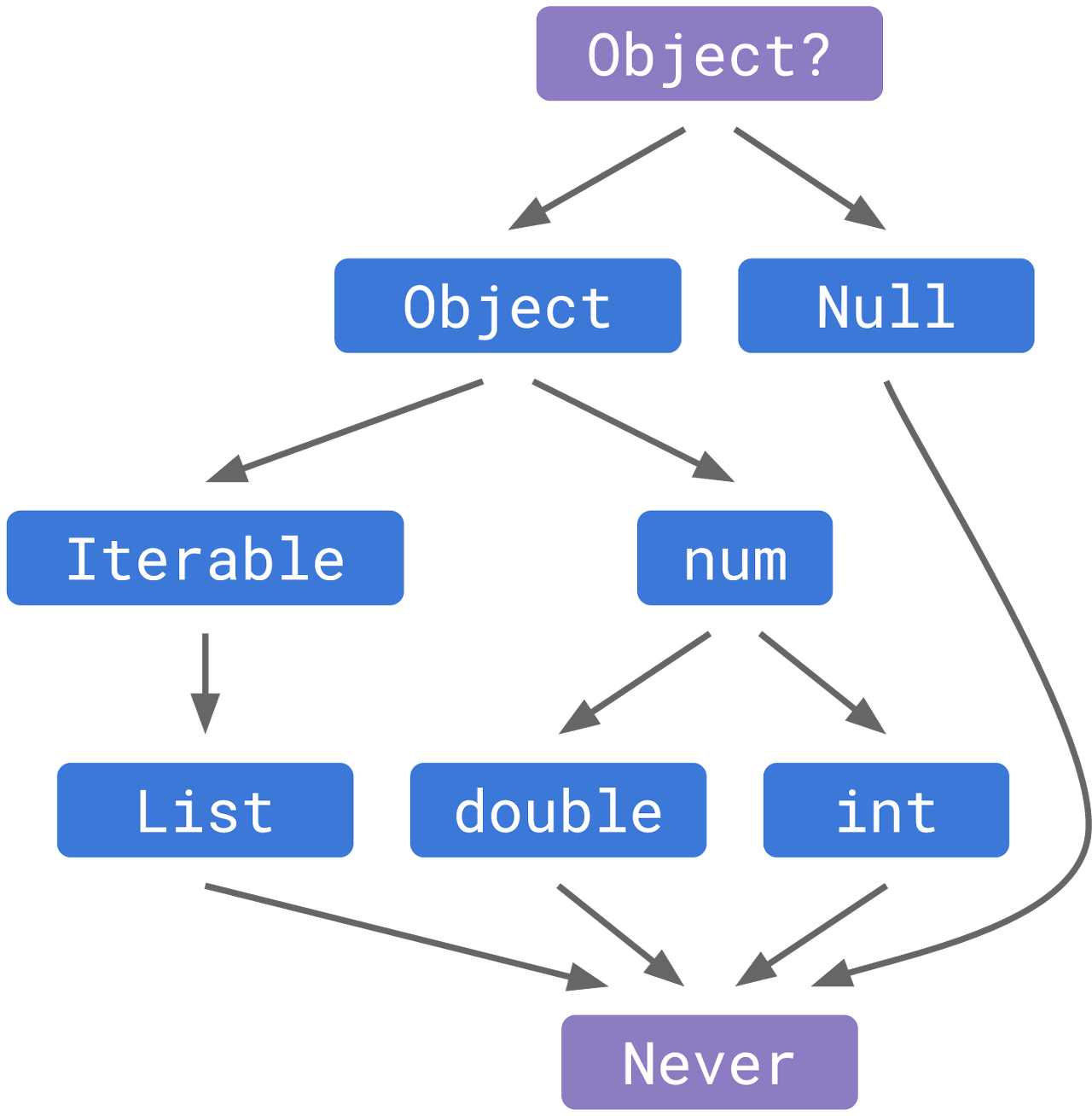
또한 최하단에 Never라는 타입이 오게 되었는데 사실상 추상적인 개념이라고 보아야할 듯 싶다.
null이 별도 타입 처리되면서 강조되는 문법들
코드랩 한 번 쫙 돌려주면 게임 끝
https://dart.dev/codelabs/null-safety
Null safety codelab
Learn about and practice writing null-safe code in DartPad!
dart.dev
exception으로 처리
일반적으로 그냥 null 잡아서 throw Exception해도 된다.
int getLength(String? str) {
if (str == null) {
throw Exception("str is null");
}
return str.length;
}
Nullish coalescing operator (??)
??를 통해 null일 경우 할당할 값을 지정할 수 있음
int? nullableVar = null;
int a = nullableVar ?? 1;
print(a);
Optional chaining (?.)
int? a = null;
print(a?.toString());
null assertion (!)
!를 통해 non-null assertion을 할 수 있음. 당연히 런타임에 확실하게 null이 절대 들어올 일 없다고 확신해야만 사용해야 함.
int? couldBeNullButIsnt = 1;
List<int?> listThatCouldHoldNulls = [2, null, 4];
int a = couldBeNullButIsnt;
int b = listThatCouldHoldNulls.first!; // first item in the list
int c = couldReturnNullButDoesnt().abs(); // absolute value
Generic과 관련된 nullable 예시
List<int> a = [3, 4, 1, 5];
List<int>? b = null; // List 자체가 null이 될 수 있다
List<int?> c = [1, 3, null, 4]; // 원소에 null이 들어올 수 있다
List<int?>? d = null; // List 자체가 null이 될 수도 있고, List가 있더라도 원소 중 null이 존재할 수 있다.
late 키워드
써보니 이 녀석은 "곧 할당 될거니까 nullable 처리 안해줘도 그냥 좀 넘어가라"라는 의미다.
class Meal {
// late 처리가 없다면non-nullable 필드는 반드시 초기화 되어야 한다고 경고뜸
late String _description;
set description(String desc) {
_description = 'Meal description: $desc';
}
String get description => _description;
}
순환 참조에 있어서 late 활용
그러니까 Team은 Coach가 있어야하고 Coach는 Team이 있는, 순환 참조의 형태인데 이럴 경우 late 처리를 해줘야한다.
안해주면 초기화하라고 경고 뜬다
class Team {
late final Coach coach;
}
class Coach {
late final Team team;
}
void main() {
final myTeam = Team();
final myCoach = Coach();
myTeam.coach = myCoach;
myCoach.team = myTeam;
print('All done!');
}
late를 활용한 lazy 초기화
(https://dart.dev/null-safety/understanding-null-safety#lazy-initialization)
int _computeValue() {
print('In _computeValue...');
return 3;
}
class CachedValueProvider {
// 여기에 late 키워드를 붙이면, 요구하기 전까지 _computeValue 실행을 미룬다.
final _cache = _computeValue();
int get value => _cache;
}
void main() {
print('Calling constructor...');
var provider = CachedValueProvider();
print('Getting value...');
print('The value is ${provider.value}!');
}감이 오겠지만 late를 사용하면 _computeValue는 print('The value is ${provider.value}!');에 의해 호출되어 필요해질 때 실행된다.
추가적으로
typescript 처럼 flow analysis 분석해줘서 type narrowing이 된다. 너무 편함!
ref)